Rosacea: A Complete Guide to Care and Treatment for Healthy Skin
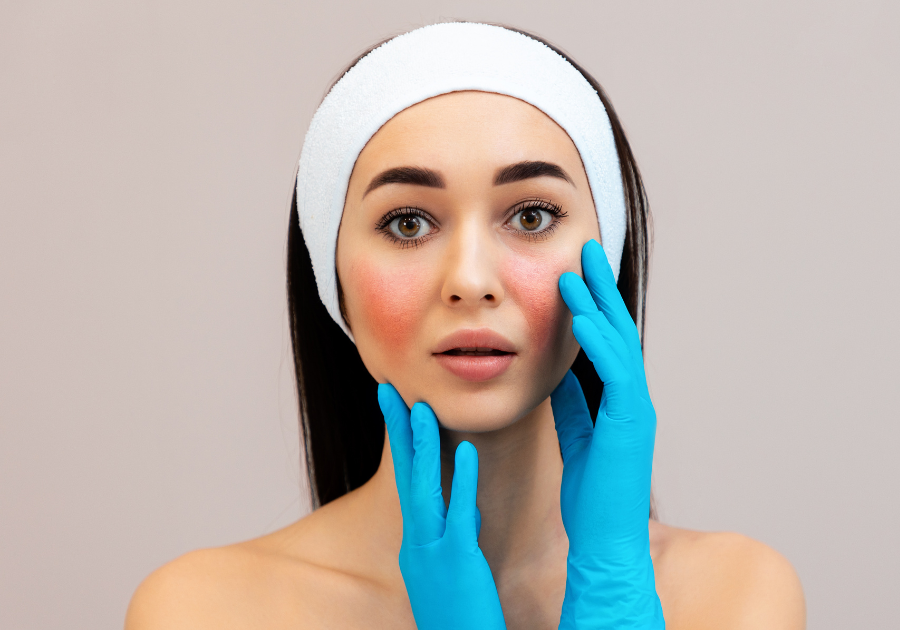
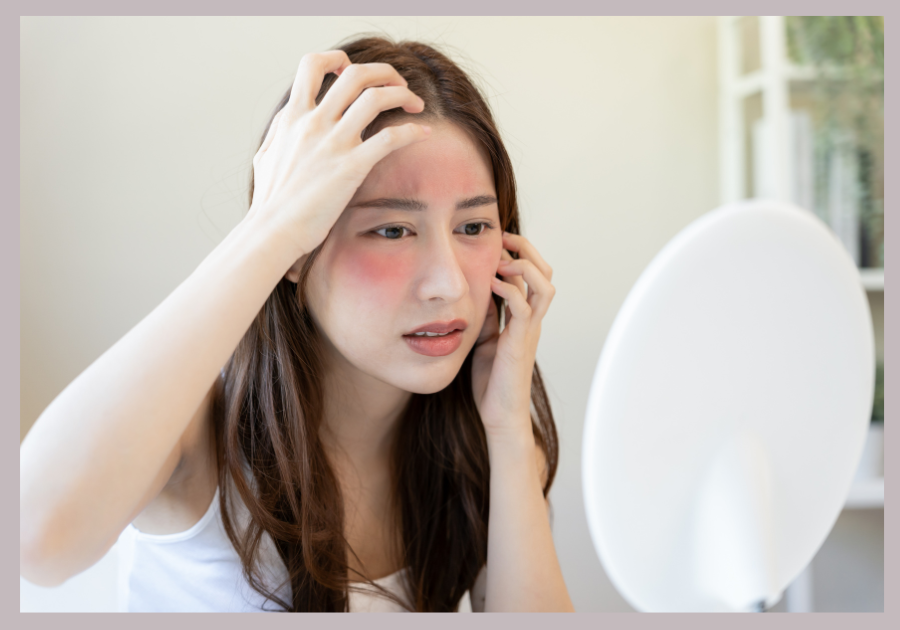
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by redness, inflammation, and in some cases, pustules and skin thickening, rosacea can cause discomfort and significantly impact self-esteem. This article provides a detailed look at what rosacea is, its causes, symptoms, types, treatments, and essential daily care tips for managing this condition effectively.
1. What is Rosacea?
Definition:
Rosacea is a chronic dermatological condition that primarily affects the face. It manifests through redness, visible blood vessels, and in more severe cases, papules and pustules that resemble acne.
Prevalence:
While anyone can develop rosacea, it is more common in fair-skinned adults, especially women, aged 30 to 50.
2. Causes of Rosacea
Genetic Factors:
Genetic predisposition can play a significant role in the development of rosacea. People with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it.
Environmental Factors:
Certain environmental factors such as sun exposure, extreme temperatures, wind, and pollution can trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms.
Lifestyle Factors:
Spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, caffeine, and emotional stress are known to trigger rosacea flare-ups.
Microorganisms:
Research suggests that the Demodex folliculorum mite, found on human skin, and the Helicobacter pylori bacterium, present in the gastrointestinal tract, may be associated with the development of rosacea.
Immune System:
Rosacea may be related to an abnormal immune response, where the immune system overreacts to environmental or microbial stimuli.
3. Symptoms of Rosacea
Facial Redness:
Persistent redness, usually on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin, is the most common symptom of rosacea.
Visible Blood Vessels:
Dilated blood vessels, known as telangiectasias, may appear on areas affected by rosacea.
Papules and Pustules:
Small red bumps (papules) or pus-filled bumps (pustules) can develop, especially during flare-ups.
Skin Thickening:
In more severe cases, the skin can become thick and uneven, particularly on the nose, a condition known as rhinophyma.
Eye Irritation:
Ocular rosacea can cause redness, dryness, burning, and sensitivity in the eyes.
4. Types of Rosacea
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea:
Characterized by persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and sensitivity.
Papulopustular Rosacea:
Characterized by redness, swelling, and acne-like breakouts (papules and pustules).
Phymatous Rosacea:
Characterized by skin thickening and irregular nodules, most common on the nose (rhinophyma).
Ocular Rosacea:
Affects the eyes, causing redness, dryness, burning, and sensitivity.
5. Diagnosis of Rosacea
Clinical Evaluation:
The diagnosis of rosacea is primarily made through a clinical evaluation by a dermatologist. Observation of symptoms and the patient’s medical history are crucial.
Complementary Tests:
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as lupus or seborrheic dermatitis.

6. Treatments for Rosacea
Topical Treatments:
- Metronidazole: An antibiotic gel or cream that helps reduce inflammation and pustules.
- Azelaic Acid: Helps reduce redness and acne-like lesions.
- Ivermectin: A cream that reduces inflammation and the count of Demodex mites on the skin.
Oral Treatments:
- Antibiotics: Tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline are often prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Isotretinoin: In severe cases, isotretinoin may be prescribed to reduce sebum production and treat persistent lesions.
Laser and Light Therapy:
Laser therapy and intense pulsed light (IPL) can help reduce redness and visible blood vessels.
Natural and Alternative Treatments:
- Green Tea Extract: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Chamomile: Has soothing properties that can help reduce irritation.
- Aloe Vera: Helps calm irritated and inflamed skin.
7. Daily Skin Care for People with Rosacea
Gentle Cleansing:
Use a gentle, fragrance-free, sulfate-free cleanser to avoid irritation. Avoid rubbing the skin during cleansing.
Moisturizing:
Apply a light, hypoallergenic, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and protect the skin barrier.
Sun Protection:
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily. Choose physical formulas with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which are less irritating.
Avoid Triggers:
Identify and avoid factors that trigger rosacea flare-ups, such as spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, and sudden temperature changes.
Suitable Products:
Opt for skincare products formulated for sensitive skin, avoiding alcohol, menthol, witch hazel, and fragrances.
8. Lifestyle and Rosacea
Balanced Diet:
Adopt a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3-rich fish.
Hydration:
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Stress Reduction:
Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, and physical exercise to help reduce stress, which can trigger rosacea flare-ups.
Physical Exercise:
Exercise regularly, but avoid activities that cause overheating or excessive sweating.
9. Treatment of Ocular Rosacea
Specific Care:
Gently wash the eyes with warm water and a dermatologist or ophthalmologist-recommended eye cleanser.
Artificial Tears:
Use artificial tears to relieve dryness in the eyes.
Avoid Irritants:
Avoid using makeup and eye products that may cause irritation.
10. Consulting a Dermatologist
Importance of Consultation:
Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for the proper diagnosis and treatment of rosacea. A dermatologist can recommend personalized treatments and monitor the treatment’s effectiveness.
Regular Follow-up:
Maintaining regular follow-ups with the dermatologist is important to adjust the treatment as necessary and ensure effective management of the condition.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a chronic condition that requires continuous and specific care. With a combination of medical treatments, daily skincare, and lifestyle adjustments, it is possible to control symptoms and improve the quality of life. Identifying personal triggers, using suitable skincare products, and consulting a dermatologist regularly are essential steps for effectively managing rosacea. With dedication and the right approach, it is possible to maintain healthy skin and minimize the impact of rosacea on daily life.

Zoe Santos is passionate about perfect skincare. Interested in skincare products, beauty techniques, and daily routines, Zoe shares tips and knowledge to help others achieve healthy and radiant skin. Her enthusiasm and informed approach make her a reference for those looking to enhance their skincare routine and achieve flawless skin.