Melasma: Identification, Causes, Treatments, and Recommended Therapies
Melasma is a common dermatological condition that manifests as dark spots on the skin, especially on the face. Although not a serious medical condition, it can significantly affect the self-esteem and quality of life of those who develop it. In this article, we will explore in detail what melasma is, its causes, how to identify it, available treatments, and recommended therapies.
1. What is Melasma?
Definition:
Melasma is a skin hyperpigmentation condition characterized by the appearance of dark and irregular spots, usually on the face. These spots can vary in color, ranging from light brown to dark brown.
Commonly Affected Areas:
The most frequently affected areas by melasma are the cheeks, forehead, nose, chin, and occasionally the neck and arms. It is more common in women, especially those of childbearing age, but it can also occur in men.
2. Identification and Symptoms
Appearance:
Melasma presents as dark, symmetrical spots with irregular borders. These spots can gradually appear and spread over time.
Types of Melasma:
- Epidermal: Pigmentation is in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis). The spots are darker and well-defined.
- Dermal: Pigmentation is in the deeper layer of the skin (dermis). The spots have a grayish color and less defined borders.
- Mixed: Combination of epidermal and dermal pigmentation.
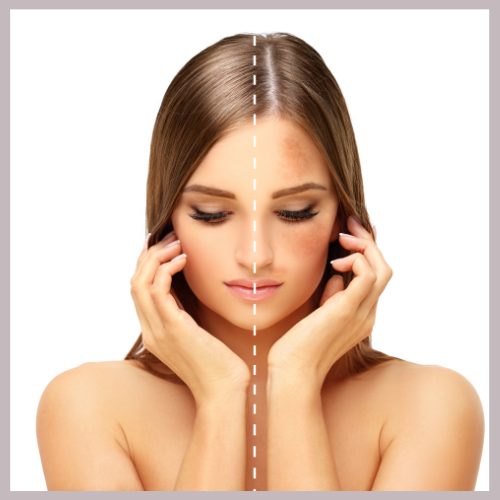

3. Causes of Melasma
Sun Exposure:
The main cause of melasma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, which stimulate melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) to increase melanin production. This results in dark spots on the skin.
Hormones:
Hormonal fluctuations are one of the main triggers of melasma. Pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives, and hormone therapy are common factors that can lead to the development of this condition.
Genetics:
Genetic predisposition also plays a significant role in melasma. Individuals with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop the condition.
Inflammation:
Any type of skin inflammation, such as acne, dermatitis, or injuries, can lead to melasma due to the inflammatory process that stimulates melanin production.
Cosmetics and Medications:
Certain cosmetic products and medications can irritate the skin and trigger or worsen melasma. It is important to use products suitable for your skin type and avoid those containing potentially irritating ingredients.
4. Diagnosis of Melasma
Clinical Evaluation:
The diagnosis of melasma is usually made by a dermatologist through a visual assessment of the spots. The doctor may use a Wood’s lamp (a special light) to determine the depth of the pigmentation.
Medical History:
The dermatologist may also ask about the patient’s medical history, including sun exposure, use of oral contraceptives, pregnancy, and family history of melasma.
5. Treatments for Melasma
Sunscreen:
Daily use of sunscreen is essential in the treatment and prevention of melasma. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher and reapply every two hours when exposed to the sun.
Depigmenting Agents:
- Hydroquinone: One of the most common treatments for melasma. It works by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production.
- Kojic Acid: A natural agent that inhibits melanin production.
- Azelaic Acid: Helps lighten dark spots and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that helps lighten the skin and protect against additional damage.
Retinoids:
Vitamin A derivatives, such as tretinoin, increase cell turnover, helping to lighten dark spots and improve skin texture.
Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels with glycolic, salicylic, or lactic acid can help exfoliate the upper layer of the skin and reduce pigmentation.
Microdermabrasion:
A procedure that uses fine crystals to exfoliate the skin’s surface layer, helping to reduce pigmentation.
Laser and Intense Pulsed Light (IPL):
Laser and IPL treatments can be effective for some people with melasma. They work by destroying the melanin pigment in the deeper layers of the skin.
6. Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Antioxidant Supplements:
Supplements like vitamin E, selenium, and lycopene can help protect the skin from free radical damage and support overall skin health.
Balanced Diet:
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidant-rich foods can help improve skin health and reduce inflammation.
Adequate Hydration:
Drinking plenty of water is essential to keep the skin hydrated and healthy, which can help reduce the appearance of melasma.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing properties, it can help reduce inflammation and lighten the skin.
- Rosehip Oil: Rich in fatty acids and antioxidants, it can help regenerate the skin and reduce dark spots.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Contains acetic acid, which can lighten the skin when used in moderation.
7. Prevention of Melasma
Regular Use of Sunscreen:
Applying sunscreen daily is the best way to prevent melasma. Choose a product with SPF 30 or higher and reapply every two hours when outdoors.
Avoid Intense Sun Exposure:
Whenever possible, avoid direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). Wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing to minimize exposure.
Care with Skincare Products:
Choose skincare products that are suitable for your skin type and avoid those containing irritating ingredients. Consult a dermatologist for specific recommendations.
Stress Management:
Stress can worsen melasma. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or physical exercise to help manage stress.
8. Common Myths About Melasma
1. Melasma is Contagious:
Melasma is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
2. Melasma Disappears on Its Own:
While some spots may lighten over time, melasma usually requires active treatment to disappear completely.
3. Only Women Develop Melasma:
Although more common in women, melasma can also affect men.
4. Melasma is Only Caused by Sun Exposure:
While sun exposure is a significant factor, hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and inflammation also play important roles in the development of melasma.
5. Home Remedies Are Ineffective:
Some home remedies, such as using lemon juice, can be harmful. It is better to opt for scientifically formulated skincare products and consult a dermatologist.
9. Melasma and Self-Esteem
The psychological impact of melasma should not be underestimated. Dark spots can affect the self-esteem and quality of life of those suffering from this condition. It is important to seek emotional support and consider psychological therapies if necessary.
10. Consulting a Dermatologist
Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for the proper diagnosis and treatment of melasma. A specialist can recommend personalized treatments based on skin type and the severity of the condition, as well as monitor the treatment’s effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
Melasma is a common but treatable condition that can be managed with a combination of prevention, topical treatments, professional procedures, and daily skincare. With patience and consistency, it is possible to significantly reduce the appearance of dark spots and improve overall skin health. Always remember to consult a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.

Zoe Santos is passionate about perfect skincare. Interested in skincare products, beauty techniques, and daily routines, Zoe shares tips and knowledge to help others achieve healthy and radiant skin. Her enthusiasm and informed approach make her a reference for those looking to enhance their skincare routine and achieve flawless skin.